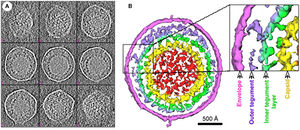
Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68
Introduction
Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68
At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki. The insertion code consists of:
Double brackets: [[
Filename: PHIL_1181_lores.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit: Electron micrograph of the Ebola Zaire virus. This was the first photo ever taken of the virus, on 10/13/1976. By Dr. F.A. Murphy, now at U.C. Davis, then at the CDC.
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
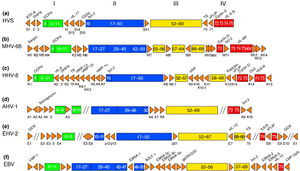
Genomic Structure of MHV-68
The complete genome of MHV-68 has been sequenced and it has been calculated that at least 75% of its gene products are homologous to HHV-8 and HVS. (1) While multiple viruses within the gammaherpesvirus subfamily have genes arranged co-linearly, there are open reading frames (ORFs) that are virus-specific. (1) ORFs are key in analyzing the gene products of latent and lytic virus cycles, and determining what stimulates the switch from one cycle to the other. Within the gammaherpesvirus subfamily, there is a division between gamma-2 and gamma-1 herpesviruses that is determined by genomic sequencing. The main basis for the genomic distinction within the subfamily is the mechanistic differences in activation from latency to lytic cycles as evidenced by the encoding of gene products. (1)
Open reading frames of significance in MHV-68 include M1, M2, M3, M7, M11, and ORF37 and ORF73. M1 is homologous to the poxvirus serpin protein family, but is not necessary for beginning the latency virus cycle. Its purpose is still unclear, but its gene product may regulate apoptosis or host inflammatory response. (1)
M2 one of the few genes of MHV-68 transcribed during the virus’ lytic cycle. Most genes are transcribed during latency. The M2 locus has been identified as the target for zinc finger antiviral protein (ZAP) binding. ZAP binds to mature M2 mRNA and reduces its expression. Reduced expression of M2 may prevent activation of the lytic cycle, since M2 is overexpressed to induce reactivation. (4)
ORF M3 encodes for a protein that binds to chemokines. (8) Chemokines recruit hemotopoietic cells to infection sites, meaning they modulate immune response in a way that opposes viral infections. The M3 chemokine-binding protein is secreted abundantly to block chemokine function and has been identified as the first binding protein to be involved in chemokine interaction in herpesviruses. (8)
M7 is a virus-specific ORF that encodes for the membrane glycoprotein gp150, which plays a key role in the characteristic of the viral membrane’s attachment and fusion to host cell membrane. (1) M7 is considered a marker of late lytic replication. M11 is a bcl-2 homolog that has been shown to inhibit apoptosis in EBV and HHV-8, and it derived from host genome. The inhibition of apoptosis could function to prolong cell life to allow for an entire lytic replication cycle to occur. (1)
ORF37 encodes viral DNA exonuclease, an enzyme which involved with processing and encapsidation of viral DNA, as well as modulation of host shutoff. Host shutoff is a mechanism highly conserved in gammaherpesviruses and is utilized to provide opportunity for the virus to initiate the lytic replication cycle and infect its host. (7)
ORF73 is reported to be responsible for a gene product critically important for the initiation and continuation of latency, and is unnecessary for lytic replication cycle efficiency. (6)
Genomically, MHV-68 is unique in that at its far 5’ end there are eight tRNA-like sequences, the function of which has yet to be elucidated. The viral tRNAs could potentially be markers for latent infection. (1) Also genomically significant is the ability of gammaherpesviruses to integrate host DNA into the viral genome, as this horizontal transfer allows for continual evolution. In MHV-68 and other gamma-2 herpesviruses there are distinguishable cellular homologous gene products that has been derived from host genome. Gene products from host homologues are predicted to play a role in cell cycle and apoptosis regulation. (1) Genomic manipulation of MHV-68 DNA is useful as a model for study of ORF function by construction of deletion mutants. Gene deletion mutants are also important for investigation of MHV-68 infection mechanisms. (1)
MHV-68 Replication Cycle
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Infection Mechanisms and Immune Response
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Conclusion
Overall paper length should be 3,000 words, with at least 3 figures.
References
Edited by student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 238 Microbiology, 2009, Kenyon College.