Toxoplasma gondii: Mode of Infection and Effect on Neurological Cells
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
By [Alexander S. McQuiston]
Introduction
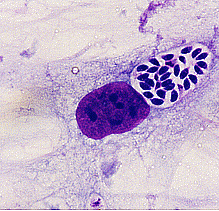
The left shows a bradyzoite cyst with the dense cyst wall surrounding the bradyzoites. The right shows tachyzoites inside the parasitophorous vacuole. Bradyzoites will slowly reproduce asexually in the cyst and tachyzoites will rapidly reproduce asexually CDC.
Life Stages
How T. gondii Infects Host Cells
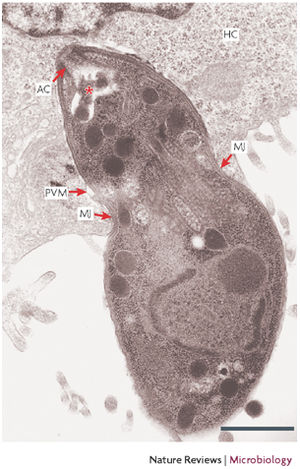
This displays a tachyzoite invading a target cell. The apical pole is already inside the host, but the rest of the cell has not been encapsulated. Constriction can be seen in the middle of the tachyzoite which makes invasion slightly more difficult NATURE.
T. gondii's Effect on the Brain
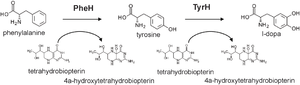
Tyrosine and phenylalanin hydroxylase catalytic reactions. Phenylalanine hydroxylase converts phenylalanine in to tyrosine, and tyrosine hydroxylase converts tyrosine to L-DOPA. Tyrosine hydroxylase controls the rate limiting step in this catalysis. PLoSONE.
