Cauliflower mosaic virus
Introduction
By Alan Brennan
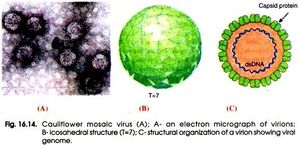
The topic of my research is the Cauliflower Mosaic Virus (CaMV). The goal of my research is to identify as well as learn about the structure and function of the Cauliflower Mosaic Virus. Learning of its processes and functions could lead to further studies in transgenic research and increased agricultural efficiency.
Taxonomy
Domain: Virus
- Group: VII
- Family: Caulimoviridae
- Genus: Caulimovirus
- Species: Cauliflower mosaic virus
- Genus: Caulimovirus
- Family: Caulimoviridae
Description and Significance
Mosaic plant diseases are common diseases that occur during warmer months which are caused by plant mosaic viruses. These plant mosaic viruses are identified in plants based on their “mottling” and discoloration of leaves (Britannica). Viruses may also cause leaf deformity, smaller produce and stunted growth. This could lead to plant death and a reduction of crop production which is why the study of mosaic viruses are essential to improve agriculture by both quantity and quality.
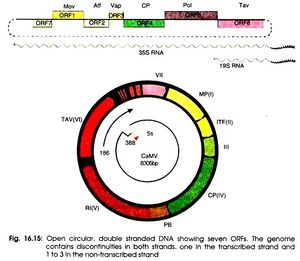
Cauliflower Mosaic Virus (CaMV), specifically, effects the Brassicaceae family and impacts a host range including crops such as broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower and turnips.Cauliflower mosaic virus is classified as a Group VII. pararetrovirus. This means the virus requires transcription from its DNA genome to RNA and then reverse transcriptase to transcribe RNA back into DNA genomes in order to produce progeny virions (Slonczewski). It was the first plant virus discovered to utilize a DNA genome and replicate via reverse transcriptase. Cauliflower mosaic virus is usually transmitted from plant to plant via aphid feeding, where virions make their way to insert themselves into the plants nuclear envelope where they inhibit growth and structure of the host.
Cauliflower mosaic virus has been negatively impactful worldwide. Previous studies have shown that CaMV cause a reduction of 25-59% sellable cauliflower heads in Brittany, France as well as a reduction of 60-90% of sellable turnips in the Czech Republic (“Cauliflower Mosaic”). Breakouts of disease can be devastating to agriculture and national economies. Studying and researching this virus could prevent disease and possibly stop the next potato famine of the cauliflower plant.
Cauliflower Mosaic Virus possesses a highly sought after efficient promoter for gene transcription that can be used in an effort to produce transgenic plants (Slonczewski). Transgenic plants are used in order to receive benefits such as producing better yield, quality as well as resistance to insects, diseases and herbicides (Mondal, Sudhadip.).Currently, about 10% of cruciferous vegetables are infected with Cauliflower Mosaic Virus in order to give the host plant pesticide resistance.
Every point of information REQUIRES CITATION using the citation tool shown above.

Section 2
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 3
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 4
Conclusion
References
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2018, Kenyon College.
