Change in the Pharyngeal Microbial Environment after a Tonsillectomy
Introduction
By Lindsey Abramson
Palatine tonsils are spheres of lymphoid tissue that sit in the back of the pharynx, or throat area, and play a huge role in the immune system due to their proximity to ingested or inhaled pathogens [1]. The immune cells on the tonsils help to filter and destroy bacteria and viruses by producing antibodies [1]. Tonsillectomies, the surgical removal of the tonsils, are performed on individuals with recurrent tonsillitis infections, recurrent strep throat, enlarged tonsils, and other issues such as cancerous cells [2]. The goal of this radical procedure is the eradication of bacteria assuming antibiotics have been frequently used and failed / resistance was developed [3]. Streptococcus pyogenes (also called group A streptococci, or GAS) is the causative agent bacterium of strep throat, one of the leading causes that push individuals towards an elective tonsillectomy [4]. Although viruses are also common, other problematic bacteria include: Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa [3]. Bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus can produce biofilms on the tonsils and can cause antibiotic resistance in the pharynx and make recurrent strep throat tonsillitis possible [3]. Within this wiki page, the pharyngeal microbial environment will be investigated before and after a tonsillectomy.
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococci, or GAS), a gram-positive bacteria, is the causative agent of strep throat and tonsillitis [4][5]. GAS falls under the classification of Firmicutes (Bacillota, “tough skin”) and contains a very thick cell wall containing 10-20 layers of peptidoglycan [4]. GAS is a worldwide public health concern due to its virulence and ability to lead to more severe infections [4][5]. Such infections like rheumatic fever can occur due to repeated GAS infections [5]. Rheumatic fever occurs after a throat infection when the M surface protein on GAS binds to a B-cell receptor on the heart and is taken up by mistake due to its resemblance to heart antigens (“cardiac-like epitope” on the M protein) [4]. GAS spreads by aerosol droplets through close or direct human to human contact [5]. The effective adhesion and attachment of GAS allows the bacteria to form microcolonies and biofilms [5]. It is hypothesized the GAS attaches through a two step process where there is first a longer range hydrophobic interaction that mediates pili attachment followed by a more specific high affinity binding [5]. Biofilms are colonies of adjacent bacteria sticking to one another attached to a surface. The biofilm formation abilities of GAS has not been extensively studied, however, it has become apparent that the pathogenesis of the biofilm may lead to recurrent infection [5]. GAS biofilm formation is regulated by a complex process including transcriptional regulation in response to environmental conditions such as temperature, PH, and oxygen presence [5]. Recent research has looked into the possibility of creating a vaccine that would inhibit either the adhesion of GAS or the biofilm formation in order to reduce the rates of tonsillitis, strep throat, and other more severe infections caused by GAS [5].
What is a Tonsillectomy?
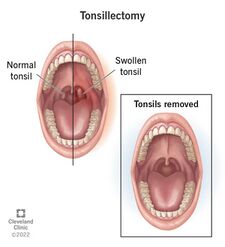
A tonsillectomy is the surgical removal of the palatine tonsils which is performed as a last resort invasive effort to fight recurrent tonsillitis infection, cancer, and other issues that cannot be solved via antibiotics or the normal functions of the immune system [2]. Tonsillectomies previously were the most popular procedure used to combat respiratory disease, however, now the prevalence of such procedures has decreased to less than one half of the number from 40 years ago [6]. The 20-30 minute procedure includes the use of general anesthesia, and the severing of the mucous membrane by electrocautery, or cold-knife cutting, or snare pulling, and then more electrocautery or sutures to stop the bleeding [7]. Due to the extremely high risk factors and complications that are associated with this procedure, it is only recommended if certain requirements are met.
The Mayo clinic defines its criteria for surgery as the following:
-seven episodes of tonsillitis in a single year, or
-five episodes of tonsillitis in each of two consecutive years, or
-three episodes of tonsillitis in each of three consecutive years [6].
After the procedure, painful swallowing and a sore incision site is to be expected. As is dehydration if fluid intake is decreased and possibly nausea [6]. The greatest concern comes from the risk of hemorrhage, which can arise at any moment after surgery when the scabs covering the incision site start to flake off [6]. Post tonsillectomy hemorrhage, which varies in risk from 0.28%-20%, is always considered an emergency and requires immediate attention and likely surgical intervention [8]. Individuals over the age of twelve are at greater risk for complication and higher levels of pain, due to the buildup of scar tissue on the tonsils themselves and an overall larger surface area [8]. Therefore, some doctors do not recommend this procedure for adults unless absolutely necessary. Furthermore, there are mixed opinions from pediatricians and ENT’s in regards to the role of tonsils in the body and long-term effects on the immune system after a tonsillectomy [9].
Pre-Tonsillectomy Microbial Environment
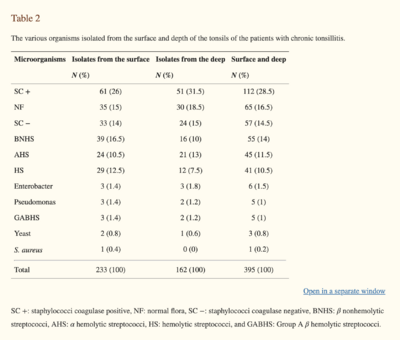
A normal or "healthy" pharyngeal environment, or more specifically, a oropharyngeal environment, consists of both “aerobic and anaerobic bacteria such as α-hemolytic and nonhemolytic streptococci, coagulase negative staphylococci, Neisseria, Flavescens, Corynebacterium, Actinomyces, Leptotrichiae, and Fusobacterium species” [10].
It should be first noted that the bacteria that causes tonsillitis can inhibit both the surface of the tonsil as well as deeper tissue[10]. This can cause issues when the prescribed antibiotics only target surface bacteria[10]. Therefore both the surface and deep tissue bacteria cultures need to be considered when analyzing the difference in microbial environments. Although tonsillectomies treat recurrent tonsillitis due to bacterial infection, it is also important to recognize that they treat Sleep-Disordered Breathing (SDB) as well, which stems from many causes, including large tonsils[11].One specific studyanalyzed the tonsils of patients that were receiving a tonsillectomy due to recurrent tonsillitis. Both surface level and deep level samples were collected to quantify the various types of bacteria found during the time of the procedure on the infected tonsils. The majority of bacteria found on the surface were the same as what was found within the tissue [11]. The most common isolated bacterial pathogens include: staphylococci coagulase positive and by β nonhemolytic streptococci [11].
Post-Tonsillectomy Microbial Environment
Karaman et al., investigated the effect of tonsillectomy on the oropharyngeal flora in children. Throat swabs were collected from 31 individuals prone to recurrent tonsillitis prior to the operation as well as one month post-tonsillectomy [12]. There was surprisingly no significant difference in the pre and post operative prevalence of aerobic pathogenic oropharyngeal bacteria [12]. The Neisseria species (part of the normal bacterial flora) did decline but not significantly, whereas the anaerobic bacteria, B fragilis did significantly decrease [12]. This could suggest that the bacteria flora may revert back to what is expected from a “healthy” individual, as increased anaerobic bacteria can be a potential risk for upper respiratory infection [12].
Another study analyzed the immune systems of 34 children after a range of 4-6 years following a tonsillectomy. Levels of the antibodies IgG, IgM, and IgA were quantified from blood samples and found to be significantly lower in individuals who underwent a tonsillectomy as compared to those who did not [9]. Having reduced levels of these antibodies could make an individual more susceptible to infection which then calls into question the risks associated with a tonsilectomy [9].
Success Rates
Conclusion
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Masters KG, Zezoff D, Lasrado S. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Tonsils. 2023. StatPearls Publishing.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Brietzke, S.E. and Andreoli, S.M., 2021. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the change in pharyngeal bacterial cultures after pediatric tonsillectomy. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, 164(2), pp.264-270.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Yildizoglu, U., Polat, B., Gumral, R., Kilic, A., Tosun, F. and Gerek, M., 2015. Effect of antibiotic use on bacterial flora of tonsil core in patients with recurrent tonsillitis. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, 272, pp.1525-1528.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Slonczewski, S.L, Foster, J.W, and Zinser, E, 2024. Microbiology an evolving science, sixth edition. W.W. Norton and Company.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 Brouwer, S., Barnett, T.C., Rivera‐Hernandez, T., Rohde, M. and Walker, M.J., 2016. Streptococcus pyogenes adhesion and colonization. FEBS letters, 590(21), pp.3739-3757.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Stuck, B.A., Windfuhr, J.P., Genzwürker, H., Schroten, H., Tenenbaum, T. and Götte, K., 2008. Tonsillectomy in children. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, 105(49), p.852.
- ↑ Younis, R.T. and Lazar, R.H., 2002. History and current practice of tonsillectomy. The Laryngoscope, 112(S100), pp.3-5.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Liu, J.H., Anderson, K.E., Willging, J.P., Myer III, C.M., Shott, S.R., Bratcher, G.O. and Cotton, R.T., 2001. Posttonsillectomy hemorrhage: what is it and what should be recorded?. Archives of Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery, 127(10), pp.1271-1275.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Radman, M., Ferdousi, A., Khorramdelazad, H. and Jalali, P., 2020. Long-term impacts of tonsillectomy on children's immune functions. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 9(3), pp.1483-1487
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Gul, M., Okur, E., Ciragil, P., Yildirim, I., Aral, M. and Kilic, M.A., 2007. The comparison of tonsillar surface and core cultures in recurrent tonsillitis. American journal of otolaryngology, 28(3), pp.173-176.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Shishegar, M. and Ashraf, M.J., 2014. Posttonsillectomy bacteremia and comparison of tonsillar surface and deep culture. Advances in preventive medicine, 2014.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Karaman, E., Enver, O., Alimoglu, Y., Gonullu, N., Bahar, H., Torun, M.M. and Isildak, H., 2009. Oropharyngeal flora changes after tonsillectomy. Otolaryngology--Head and Neck Surgery, 141(5), pp.609-613.
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski,at Kenyon College,2024
