Ebola Transmission
Introduction
The Ebola virus is a relatively recently described, severe disease-causing pathogen that poses a huge threat to human health mostly within central Africa. This is, in part, due to its high mortality4 and lack of affordable treatment options. Ebola is considered a Biosafety level 4 (BSL-4) agent; classifying it among the most threatening pathogens that exist in the world today. Agents within this category pose severe threats to human health and can be fatal due to the lack of available vaccines. There are five known Ebola species within the family Filoviridae and all of the species within the family cause varying degrees of viral hemorrhagic fever illnesses.[4]
Virus Structure
The Ebola virus has an RNA genome that codes for at least seven proteins and is enclosed in a nucleocapsid[3]. Four of the virus’ proteins are thought to comprise the capsid. The capsid allows the transcription and the translation of the viral genome and is therefore the principle player in the virus’ pathogenicity4. In addition, the virus has been shown to impair the immune function of the body by way of its infection of the phagocytic cells. The nucleocapsid and viral proteins move to new sites of infection and form themselves into virons where they can then go on to infect around the host body.
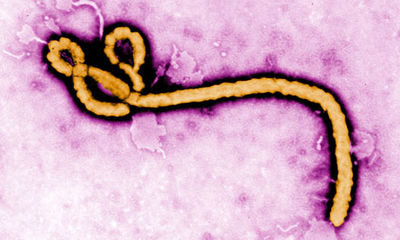
The virus forms many long rods and is much longer than it is wide and is often photographed in a hooked or curved form. The virus is around 80nm in diameter and can be of varying lengths ranging from 900-100nm. Ebola does not produce its own cell membrane and instead steals some of its host membrane to survive. [4]
Containment and Transmission
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Possible Treatments
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure
Conclusion
In today's world Ebola is still a huge problem that faces many developing nations within Africa. In 2012 alone there were 5 outbreaks of Hemorrhagic Fevers around the world and 3 of them were due to the Ebola virus.7
References
3. "Ebola virus: from discovery to vaccine". Nature Reviews Immunology 3. 2003. p. 667- 85.
Edited by (Victoria Rose Gawlik), a student of Nora Sullivan in BIOL187S (Microbial Life) in The Keck Science Department of the Claremont Colleges Spring 2013.