Bacterial Transcription Factors against Reactive Oxygen Species: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.<br> | Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.<br> | ||
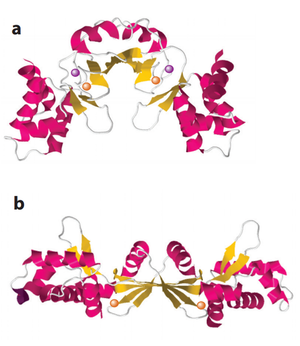
<br>[[Image:PerR.png|thumb|300px| | <br>[[Image:PerR.png|thumb|300px|right|Structure of PerR in <i>Bacillus subtilis</i>. (a) holoenzyme (b) demetallated (Manganese removed) enzyme. The orange balls are Zn and the purple ones are Mn]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 22:19, 25 April 2016
Overview
By Jiayu Chen
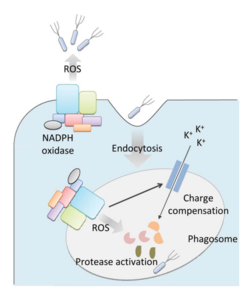
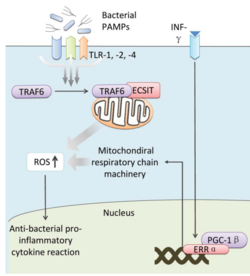
Bacteria live in a world full of toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS), including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2-), and hydroxyl radicals. ROS can cause severe damage to all kinds of cell components, including nucleic acids, lipids and proteins (Halliwell, 2006). These highly reactive species are generated endogenously by accidental autoxidation of flavoproteins, a group of non-respiratory redox enzymes (Figure 1) (Seaver and Imlay, 2004; Korshunov and Imlay, 2010). Thus, aerobic bacteria have evolved to maintain high concentration of enzymes that keep intracellular ROS below a lethal level. However, various conditions are known to increase these species above such threshold, inflicting oxidative stress to the bacteria, a phenomenon called “oxidative burst” (Apostol et al., 1989). One of the major scenario is when bacteria encounter ROS generated by the immune system of their host as a defensive weapon. In human, phagocytes including neutrophils use NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2) complex as one of the major enzyme mediating the immune response by generating antimicrobial ROS (Lam et al., 2010). The resultant ROS would be secreted either outside of the cell as a trap to kill bacteria, or into phagolysosome where internalized bacteria would be degraded (Reeve et al., 2002; Brinkmann et al., 2004). Another situation that may happen during bacterial infection is the ROS generated by the mitochondria. Such defensive mechanism is mediated by many signaling molecule in the Toll pathways including several Toll-like receptors (TLRs), tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and evolutionarily conserved signaling intermediate in Toll pathways (ECSIT). The activation of Toll pathways resulted in increased cellular ROS as well as anti-bacterial pro-inflammatory cytokine reaction in the nucleus (West et al., 2011). Pro-inflammatory Th1 cytokine IFN-γ is also involved as a transcriptional regulator via activation of estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα) and PPARγ-coactivator-1β (PGC-1β) in the nucleus. Such interaction induces the genes that encode mitochondrial respiratory chain machinery and thus increase cellular ROS concentration (Sonoda et al., 2007).
Therefore, bacteria have developed defensive systems to deal with such situations. One mechanism is ROS inducible transcriptional factors that regulate gene expression of a variety of enzymes to respond to the oxidative stress. Three redox-sensitive transcription factors in bacteria have been intensively studied: OxyR and PerR against H2O2, and SoxR against O2- [1].
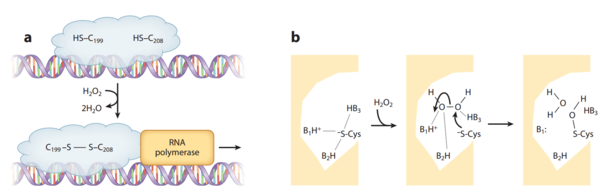
OxyR is induced by H2O2 and activated by reversible disulfide bond formation in its active site (Choi et al., 2001). OxyR is widely distributed in Gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli. The binding of OxyR to DNA generally turns on the gene expression of a large range of oxidative stress defensive enzymes (Zheng et al., 1998). Recent research also has shown that Gram-negative bacteria Vibrio vulnificus, facultative aerobes, contain two OxyR-type regulators with similar sensory mechanism but different sensitivity in order to fine-tune the expression of genes against H2O2 pressure (Kim et al., 2014).
PerR is the equivalent H2O2 sensor protein in many Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. When PerR is in its reduced form, its binding to DNA generally serves as an inhibitor of the expression of target genes. PerR is activated by oxidation of its regulatory metal, either Fe2+ or Mn2+, which leads to conformational change in the protein and dissociation from DNA, thus relieving the inhibition and initiating transcription of H2O2 defensive genes [2] (Li and Helmann, 2014).
SoxR is conserved widely in both proteobacteria and actinobacteria with an O2- sensitive metal complex in its active site. The binding of SoxR to DNA induces the transcription of a secondary transcription factor, SoxS, which activates a group of enzymes suppressing the level of O2- (Greenbert et al., 1990; Tsaneva and Weiss, 1990; Blanchard et al., 2007).
Sample citations:
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
Defending against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Every point of information REQUIRES CITATION using the citation tool shown above.
Section 2
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 3
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 4
Conclusion
References
- ↑ Imaly, J.A.: Transcription factors that defend bacteria against reactive oxygen species 2015. Annual Review of Microbiology 69: 93–108.
- ↑ Ji et al.: Staphylococcus aureus PerR Is a Hypersensitive Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor using Iron-mediated Histidine Oxidation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 290: 20374-20386.
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2016, Kenyon College.