Candidatus Cardinium: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why you think it is important. | Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why you think it is important. | ||
‘Candidatus Cardinium’ is a bacterium from the Bacteriodetes group. It is involved in reproduction alterations of anthropod host organisms including cytoplasmic incompatibility, parthenogenesis, and feminization. | |||
This bacterium is often located within the reproductive tissues of the host. It is often found with other anthropod-associated Bacteroidetes that alter host biology. Distantly related hosts can harbor closely related Cardinium. Closely related Cardinium also tend to cluster with closely related hosts. | |||
-Distantly related hosts can harbor closely related Cardinium | |||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
‘Candidatus Cardinium’ has linear 1364 bp DNA sequence. | |||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
Revision as of 19:05, 19 April 2011
Classification
Domain (Bacteria); Super Phylum (Bacteroidetes/Chlorobi group); Phylum (Bacteroidetes); Class (Bacteroidetes); Order (Bacteroidales); Family (Bacteroidaceae); Genus (Candidatus Cardinium)
Species
Candidatus Cardinium
Description and Significance
Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why you think it is important.
‘Candidatus Cardinium’ is a bacterium from the Bacteriodetes group. It is involved in reproduction alterations of anthropod host organisms including cytoplasmic incompatibility, parthenogenesis, and feminization.
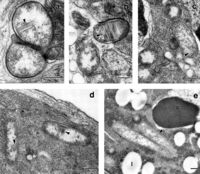
This bacterium is often located within the reproductive tissues of the host. It is often found with other anthropod-associated Bacteroidetes that alter host biology. Distantly related hosts can harbor closely related Cardinium. Closely related Cardinium also tend to cluster with closely related hosts.
Genome Structure
‘Candidatus Cardinium’ has linear 1364 bp DNA sequence.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
-Specifically located in reproductive tissues of host.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
-Capacity to feminize (ex. B. californicus).
-Does not have a negative effect on fitness of organism.
-May contribute to host organism by adding insectiside resistance.
References
Author
Page authored by Benjamin Lowe & Brian Lovett, students of Prof. Jay Lennon at Michigan State University.
<-- Do not remove this line-->
