Candidatus Cardinium: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ==Ecology and Pathogenesis== | ||
This bacteria is located within the reproductive tissues of the host organism. Commonly found in arthropods. Often transmitted from mother to daughter.‘Candidatus Cardinium' has the capacity to feminize the host organism. Feminization can be functional or genetic alone. In some cases, it has been shown to increase fecundity of the female host. This endosymbiont does not appear to have a negative effect on the host. It has been hypothesized that it confers a slight insectiside resistance to the host. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 15:51, 20 April 2011
Classification
Domain (Bacteria); Super Phylum (Bacteroidetes/Chlorobi group); Phylum (Cytophaga-Flavobacterium-Bacteroides); Class (Bacteroidetes); Order (Bacteroidales); Family (Bacteroidaceae); Genus (Candidatus Cardinium)
Species
Candidatus Cardinium
Description and Significance
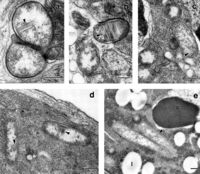
‘Candidatus Cardinium’ is a bacterium from the Bacteriodetes group. It is involved in reproduction alterations of arthropod host organisms including cytoplasmic incompatibility, parthenogenesis, and feminization.
This bacterium is often located within the reproductive tissues of the host. It is often found with other arthropod-associated Bacteroidetes that alter host biology. Distantly related hosts can harbor closely related Cardinium. Closely related Cardinium also tend to cluster with closely related hosts.
Genome Structure
‘Candidatus Cardinium’ has linear 1364 bp DNA sequence.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Ecology and Pathogenesis
This bacteria is located within the reproductive tissues of the host organism. Commonly found in arthropods. Often transmitted from mother to daughter.‘Candidatus Cardinium' has the capacity to feminize the host organism. Feminization can be functional or genetic alone. In some cases, it has been shown to increase fecundity of the female host. This endosymbiont does not appear to have a negative effect on the host. It has been hypothesized that it confers a slight insectiside resistance to the host.
References
Author
Page authored by Benjamin Lowe & Brian Lovett, students of Prof. Jay Lennon at Michigan State University.
<-- Do not remove this line-->
