Candidatus Mellornella promiscua: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Genome Structure== | ==Genome Structure== | ||
Candidatus Mellornella promiscua has a circular genome about 1,013,119 base pair in length. It encodes 899 protein coding genes, 1 pseudo gene, 3 ncRNA genes, 3 rRNA genes, and 33 tRNA genes. This encodes functional proteins that help with metabolism, synthesis, energy, DNA processing, secretion, translation, signaling, recognition, regulation, structure, motility, resistance, and others. Region I is composed of mix of metabolic and structural proteins. Region II is the largest region, and is composed of two protein groups: nitrogen processing and biosynthesis. Region III is signaling functions. | |||
==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ==Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle== | ||
Revision as of 00:53, 10 November 2023
Classification
Prokaryota; Proteobacteria; Alphaproteobacteria; Rickettsiales; Anaplasmataceae.
Species
|
NCBI: [1] |
Genus species
Description and Significance
Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why you think it is important.
Genome Structure
Candidatus Mellornella promiscua has a circular genome about 1,013,119 base pair in length. It encodes 899 protein coding genes, 1 pseudo gene, 3 ncRNA genes, 3 rRNA genes, and 33 tRNA genes. This encodes functional proteins that help with metabolism, synthesis, energy, DNA processing, secretion, translation, signaling, recognition, regulation, structure, motility, resistance, and others. Region I is composed of mix of metabolic and structural proteins. Region II is the largest region, and is composed of two protein groups: nitrogen processing and biosynthesis. Region III is signaling functions.
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
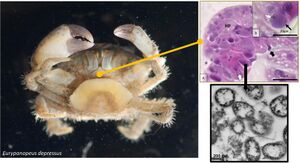
Identification during a transmission electron micrograph showed multiple bacterial vacuoles expanding in the cell cytoplasm. The bacterium typically had vacuolar membrane but in advanced infections they didn't have the vacuolar membrane and directly interacted with the host cell cytoplasm. Most bacterium presented a pill-like structure expanding around the bacteria cell as well as a fibrous inclusion body. Their life cycle consist of binary fission. Region 1 of the genome contains 12 protein coding genes which also consist of metabolic proteins. The bacterium also has multiple semi-conserved biosynthetic secondary metabolite clusters.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
Author
Page authored by Maggie West, student of Prof. Bradley Tolar at UNC Wilmington.