Conexibacter: Difference between revisions
Asteinberger (talk | contribs) |
Asteinberger (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
=Description= | =Description= | ||
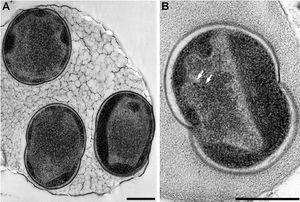
Bacteria of the genus ''Conexibacter'' are characterized as small rods with width of 0.6-0.7 µm and length of 0.9-1.2 µm. They are Gram-positive, aerobic, non-sporulating and are motile by characteristic long peritrichous flagella | Bacteria of the genus ''Conexibacter'' are characterized as small rods with width of 0.6-0.7 µm and length of 0.9-1.2 µm. They are Gram-positive, aerobic, non-sporulating and are motile by characteristic long peritrichous flagella. The type strain of this genus is ''Conexibacter woesei'' named in honor of Carl R. Woese, a pioneer with this work on the use of 16S rRNA for phylogenetic analysis. ''C. woesei'' was isolated from forest soil in Gerenzano, Italy and grows optimally at pH 7-7.5 and at 28-37ºC. | ||
The genus ''Conexibacter'' was first developed in 2003 with the discovery of the type strain ''C. woesei''. In 2012 a second species, ''Conexibacter arvalis'', was isolated from Japan field soil. Both cultures are available in pure culture. The genus is known as a very deep branch of the phylum ''Actinobacteria'' having only a 90% similarity to their next closest genus ''Thermoleiphilum'', and being only 83.8% similar to the well known genus ''Rubrobacter'', described as the only known radiation resistant thermophile. | |||
[[File:alcanivorax bork.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Alcanivorax borkumensis [1F] ]] | [[File:alcanivorax bork.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Alcanivorax borkumensis [1F] ]] | ||
Revision as of 12:52, 8 May 2015
Classification
Domain: Bacteria
Phylum: Actinobaceria
Class: Actinobaceria
Sub-Class: Rubrobacteridae
Order: Solirubrobacteriales
Family: Conexibacteraceae
Genus: Conexibacter
Species
Conexibacter woesei (DSM 14684) (type strain), Conexibacter arvalis (DSM 23288)
|
NCBI [1] |
Description
Bacteria of the genus Conexibacter are characterized as small rods with width of 0.6-0.7 µm and length of 0.9-1.2 µm. They are Gram-positive, aerobic, non-sporulating and are motile by characteristic long peritrichous flagella. The type strain of this genus is Conexibacter woesei named in honor of Carl R. Woese, a pioneer with this work on the use of 16S rRNA for phylogenetic analysis. C. woesei was isolated from forest soil in Gerenzano, Italy and grows optimally at pH 7-7.5 and at 28-37ºC.
The genus Conexibacter was first developed in 2003 with the discovery of the type strain C. woesei. In 2012 a second species, Conexibacter arvalis, was isolated from Japan field soil. Both cultures are available in pure culture. The genus is known as a very deep branch of the phylum Actinobacteria having only a 90% similarity to their next closest genus Thermoleiphilum, and being only 83.8% similar to the well known genus Rubrobacter, described as the only known radiation resistant thermophile.
Ecology and Significance
Genome Structure
|
NCBI GenBank: [2] |
C. woesei complete genome.
Metabolism
References
[1] Monciardini, Paolo, et al. "Conexibacter woesei gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel representative of a deep evolutionary line of descent withing the class Actinobacteria." 53 (2003): 569-576. Print.
Figures
[1F]
[3] [2F] [4] [3F] [5] [4F] [6] [5F] [Original Figure. Author: Pawan Dhaliwal] [6F]
http://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/File:Lorenzo.gif
[7F] [7]
Author
Page authored by Andrew Steinberger, student of Prof. Katherine Mcmahon at University of Wisconsin - Madison.