Courtney Dever and Jennifer Lopez
Classification
Kingdom Bacteria
Phylum Firmicutes
Class Bacilli
Order Bacillales
Family Paenibacillaceae
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy |
Genus species Brevibacillus laterosporus [2]
Habitat Information
Describe the location and conditions under which the organism was isolated.
Two tablespoons of an unknown soil organism were collected at a depth of approximately 1” below the soil surface on January 1, 2016 at 11:53 am from (latitude, longitude) and placed in a plastic Ziploc baggie at room temperature. Below is a picture of the area, and also a picture of the exact location where the soil was taken at the time of retrieval.
Weather conditions on January 1, 2016 at 11:53 am were as follows [5]
Wind: S14
Visibility: 10
Weather: A few clouds
Sky conditions: FEW 200
Temperature:
• Air temperature: 73°F
• Dewpoint: 34
• 6 hour max: 73
• 6 hour min: 32
Relative humidity: 24%
Pressure:
• Altimeter (in): 30.06
• Sea level (mb): 1017.8
• Precipitation (in): 0
Weather conditions also included [6] texaset.tamu.edu
ET0 or PET: 0.10 in.
Temperature max: 76 °F
Temperature min: 36°F
RH min: 17%
Solar radiation: 17.55 MJm2
Rain: 0 in.
Wind 4 am: 0.12 mph
Wind 4 pm: 6.13 mph
Soil conditions included (source: websoilsurvey.sc.egov.usda.gov):
Map Unit Name: Travis soils and urban land, 1 to 8 percent slopes
Acres in AOI: 0.1
Percent of AOI: 100%
Description and Significance
Describe the appearance (colonial and cellular), possible antimicrobial activity etc. of the organism, and why the organism might be significant.
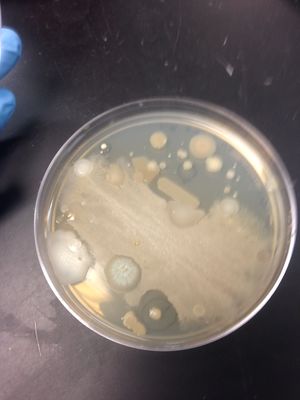
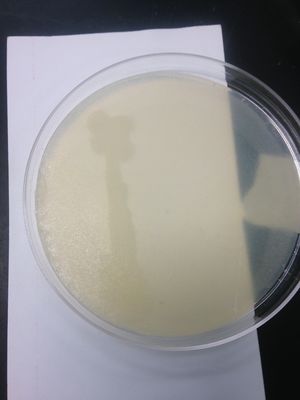
Colony morphology:
-Size: small
-Margin: round/uneven
-Elevation:convex
-Surface: smooth
-Pigment produced: none.
-Color: Whitish and opaque.
Gram stain: positive.
Endospore stain: positive.
Capsule stain: negative.
Our organism is a G+ rod (bacillus) that forms short chains of 2. It also forms endospores.
Laterosporus brevibacillus has been shown to have antimycobacterial properties in a Brazilian study. [3]
Laterosporus brevibacillus has been shown to have pesticidal uses against insects and nematodes and mollusks. [4]
Laterosporus brevibacillus is a broad spectrum antimicrobial species due to its antimicrobial uses against phytopathogenic bacteria and fungi. [4]
Genome Structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence? Include S Ribosomal sequence that you obtained from PCR and sequencing here.
BLAST Search from DNA sequencing results: >CD-Forward_G10.ab1
GATGGAGCAACGCCGCGTGAACGATGAAGGCTTTC
GGGTCGTAAAGTTCTGTTGTTAGGGAAGAAACAGTGCTATTTAAATAAGATAGCACCTTGACGGTACCTAACGAGAAAGC
CACGGCTAACTACGTGCCAGCAGCCGCGGTAATACGTAGGTGGCAAGCGTTGTCCGGAATTATTGGGCGTAAAGCGCGCG
CAGGTGGCTATGTAAGTCTGATGTTAAAGCCCGAGGCTCAACCTCGGTTCGCATTGGAAACTGTGTAGCTTGAGTGCAGG
AGAGGAAAGTGGTATTCCACGTGTAGCGGTGAAATGCGTAGAGATGTGGAGGAACACCAGTGGCGAAGGCGACTTTCTGG
CCTGTAACTGACACTGAGGCGCGAAAGCGTGGGGAGCAAACAGGATTAGATACCCTGGTAGTCCACGCCGTAAACGATGA
GTGCTAGGTGTTAGGGGTTTCAATACCCTTAGTGCCGCAGCTAACGCAATAAGCACTCCGCCTGGGGAGTACGCTCGCAA
GAGTGAAACTCAAAGGAATTGACGGGGGCCCGCACAAGCGGTGGAGCATGTGGTTTAATTCGAAGCAACGCGAAGAACCT
TACCAGGTCTTGACATCCCACTGACCGCTCTAGAGATAGAGCTTCCCTTCGGGGCAGTGGTGACAGGTGGTGCATGGTTG
TCGTCAGCTCGTGCCGTGANATGTCATA
>JL-Reverse_H10.ab1
ACCACCTGTCACCACTGCCCCGAAGGGAAGCTCTATCTCTAGAGCGGTCAGTGGGATGTCAAGACC
TGGTAAGGTTCTTCGCGTTGCTTCGAATTAAACCACATGCTCCACCGCTTGTGCGGGCCCCCGTCAATTCCTTTGAGTTT
CACTCTTGCGAGCGTACTCCCCAGGCGGAGTGCTTATTGCGTTAGCTGCGGCACTAAGGGTATTGAAACCCCTAACACCT
AGCACTCATCGTTTACGGCGTGGACTACCAGGGTATCTAATCCTGTTTGCTCCCCACGCTTTCGCGCCTCAGTGTCAGTT
ACAGGCCAGAAAGTCGCCTTCGCCACTGGTGTTCCTCCACATCTCTACGCATTTCACCGCTACACGTGGAATACCACTTT
CCTCTCCTGCACTCAAGCTACACAGTTTCCAATGCGAACCGAGGTTGAGCCTCGGGCTTTAACATCAGACTTACATAGCC
ACCTGCGCGCGCTTTACGCCCAATAATTCCGGACAACGCTTGCCACCTACGTATTACCGCGGCTGCTGGCACGTAGTTAG
CCGTGGCTTTCTCGTTAGGTACCGTCAAGGTGCTANCTTATTTAAATAGCACTGTTTCTTCCCTAACAACAGAACTTTAC
GACCCGAAAGCCTTCATCGTTCACGCGGCGTTGCTCCATCAGACTTTCGTCCATTGTGGAAAATTCCCTACTGCTGCCNC
CCGTA
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Physiology and Pathogenesis
Biochemical characteristics, enzymes made, other characteristics that may be used to identify the organism; contributions to environment (if any).
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
Biochemical Characteristics:
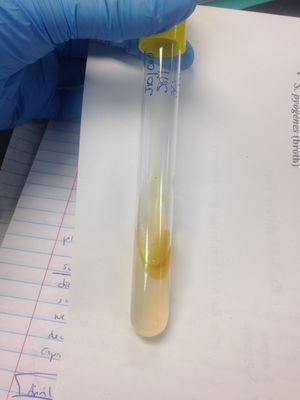
Phenol Red Broth:
•Glucose fermentation: (+) result; broth was yellow indicating glucose fermentation.
•Lactose fermentation: (-) result; broth was red—no change in broth.
•Sucrose fermentation: (-) result; broth was red—no change in broth.
problems encountered during procedure: no problems occurred during procedure.
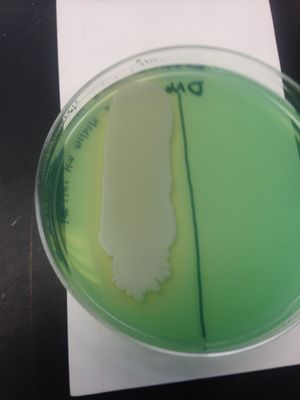
Starch Hydrolysis: (+) result; clearing was present on starch agar media; soil organism produces the α-amylase enzyme.
Casein Hydrolysis: (-) result; no clearing in skim milk agar; soil organism does not produce the casease enzyme.
Gelatin Hydrolysis: (+) result; solid broth turned to liquid; soil organism produces the gelatinase enzyme.
DNA Hydrolysis: (+) result; clearing in agar; soil organism produces the DNase enzyme.
Lipid Hydrolysis: (-) result; no clearing in Tributyrin agar; soil organism does not produce the Lipase enzyme.
Methyl Red: (-) result; broth is orange in color; soil organism does not use the mixed acid fermentation pathway, and does not produce mixed acid end-products.
Voges Proskauer (+) result; broth is red in color; soil organism utilizes the butylene glycol pathway, produces acetoin, and produces neutral end-products.
Citrate Test: (-) result, slant is green in color; soil organism does not utilize citrate as a carbon source.
SIM Tests:
•Motility (+) result; soil organism is motile as entire tube is pink.
•Indole (+) result; soil organism is able to produce indole.
•Sulfur (-) result; soil organism cannot reduce sulfur to hydrogen sulfide.
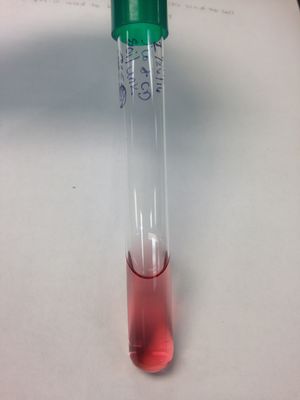
Nitrate Reduction Test: (-) result; soil organism is not able to reduce Nitrate to ammonia or molecular nitrogen; zinc was added the test tube turned red, showing a negative result for nitrate reduction.
Urea Hydrolysis: (-) result; broth is salmon in color; soil organism does not produce the urease enzyme.
Triple Sugar Iron: (K/A) result; slant is red in color, butt is orange in color; glucose fermentation with acid production; peptones/proteins catabolized aerobically (in the slant) with alkaline products (reversion).
Decarboxylation:
•Arginine (-) result; broth is yellow; soil organism does not produce arginine decarboxylase and does not ferment.
•Lysine (-) result; broth is yellow; soil organism does not produce lysine decarboxylase.
•Ornithine (-)result; broth is yellow; soil organism does not produce ornithine decarboxylase.
Oxidase Test: (+) result; soil organism can produce Cytochrome c oxidase.
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar : (-) result; organism didn't grow b/c it is G+.
Hektoen Enteric Agar (HE): (-) result; organism didn't grow b/c it is G+.
MacConkey Agar (MAC): (-) result; organism didn't grow b/c it is G+.
Phenylalanine Deaminase: (-) result; organism doesn't produce Phenylalanine deaminase.
Catalase Test: (-) result; organism doesn't produce catalase.
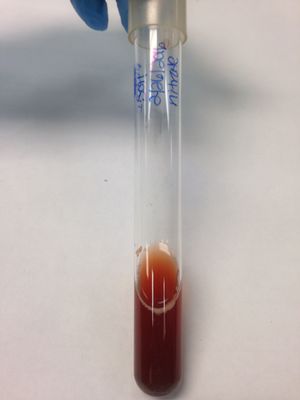
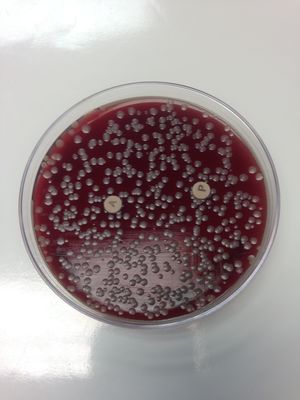
Blood Agar: (gamma) result; no clearing in the media; soil organism does not produce hemolysins.
Mannitol Salt Agar : (-) result; no growth and no fermentation.
Phenylethyl Alcohol Agar (PEA): (+) result; growth, but really slow growth.
Bile Esculin: (+) result; slant is dark brown in color; organism hydrolyzes esculin.
6.5% Salt Tolerance: (-) result; organism is not salt tolerant.
Bacitracin/Optochin: (-) result; organism produced no antibodies to A-disc or P-disc.
Antimicrobial Sensitivity/Kirby-Bauer Test:
•(-) to Triple Sulfa;
•(-) to Azlocillin;
•(-) to Ceftazidime;
•(-) to Bacitracin
problems encountered during procedure: no problems occurred during procedure.
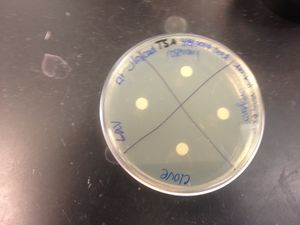
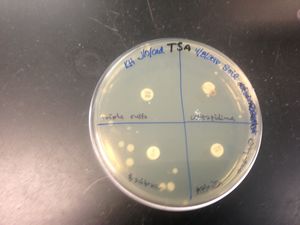
Disinfectant sensitivity:
•(-) to lavendar
•(-) to clove
•(-) to rosemary
•(-) to oregano
problems encountered during procedure: no problems occurred during procedure.
References
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi [1]
http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi [2]
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1517-83822012000400036 [3]
Ruiu, Luca "Brevibacillus laterosporus, a Pathogen of Invertebrates and a Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Species". Insects 2013, 4, 476-492; doi:10.3390/insects4030476
Retrieved from: www.mdpi.com/2075-4450/4/3/476/pdf [4]
w1.weather.gov [5]
texaset.tamu.edu [6]
Author
Page authored by Courtney Dever and Jennifer Lopez, students of Prof. Kristine Hollingsworth at Austin Community College.