Finegoldia magna: Difference between revisions
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
[https://www-nature-com.proxyiub.uits.iu.edu/articles/s41598-017-18661-8 Brüggemann, H., A. Jensen, S. Nazipi, H. Aslan, R. Meyer, A. Poehlein, E. Brzuszkiewics, M. Al-Zeer, V. Brinkmann, B. Söderquist. "Pan-genome analysis of the genus Finegoldia identifies two distinct clades, strain-specific heterogeneity, and putative virulence factors". ''Nature: Scientific Reports''. 2018. 8 :216.] | [https://www-nature-com.proxyiub.uits.iu.edu/articles/s41598-017-18661-8 Brüggemann, H., A. Jensen, S. Nazipi, H. Aslan, R. Meyer, A. Poehlein, E. Brzuszkiewics, M. Al-Zeer, V. Brinkmann, B. Söderquist. "Pan-genome analysis of the genus Finegoldia identifies two distinct clades, strain-specific heterogeneity, and putative virulence factors". ''Nature: Scientific Reports''. 2018. '''8''':216.] | ||
==Author== | ==Author== | ||
Revision as of 22:51, 20 April 2022
Classification
Domain: Bacteria
Phylum: Firmicutes
Class: Clostridia
Order: Eubacteriales
Family: Peptoniphilaceae
Genus: Finegoldia
Species: Finegoldia magna [2]
Species
|
NCBI: Taxonomy [3] |
Finegoldia magna
Description and Significance
Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why you think it is important.
Genome Structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence?
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Interesting features of cell structure; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
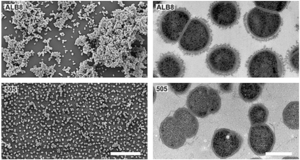
Finegoldia magna has a cell structure that is a cocci, or spherical in shape and bacilli (rod-shaped bacteria). It has a cell size that varies from 0.8µm and 1.6µm in diameter, which occur predominantly in clusters but occasionally in short chains, as in Figure 2.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
Habitat; symbiosis; biogeochemical significance; contributions to environment.
If relevant, how does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
References
Author
Page authored by Susan Reed, Nitesh Naren, Matt Millikin, students of Prof. Jay Lennon at Indiana University.