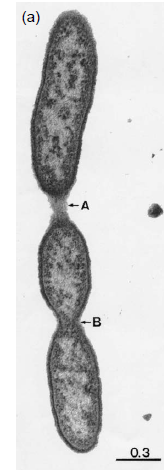
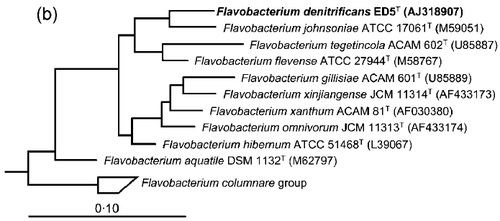
Flavobacterium denitrificans
Classification
Bacteria; Bacteroidetes/Chlorobi group; Bacteroidetes; Flavobacteriia; Flavobacteriales; Flavobacteriaceae; Flavobacterium
Species
Flavobacterium denitrificans
Description and Significance
Genome Structure
Cell Structure, Metabolism and Life Cycle
Flavobacterium denitrificans” has flat, circular and yellow colonies. It is a facultative aerobe and an active member of the soil microbial community. It is activated in the earthworm (“Aporrectodea caliginosa”) gut, an anoxic and substrate rich habitat. Flavobacterium denitrificans” carries out denitrificaiton, whish is the dissimilative reduction of nitrate and nitrite to atmospheric nitrogen. This process can also result in a significant production of nitrous oxide, a powerful greenhouse gas. Earthworms may account for more than 50% of the total nitrous oxide emitted form a soil they inhabit.
Ecology and Pathogenesis
References
Drake, Harold L., and Marcus A. Horn. "As the worm turns: the earthworm gut as a transient habitat for soil microbial biomes." Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 61 (2007): 169-189.
Horn, Marcus A., et al. "Dechloromonas denitrificans sp. nov., Flavobacterium denitrificans sp. nov., Paenibacillus anaericanus sp. nov. and Paenibacillus terrae strain MH72, N2O-producing bacteria isolated from the gut of the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa." International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology 55.3 (2005): 1255-1265.
Philippot, Laurent, Sara Hallin, and Michael Schloter. "Ecology of denitrifying prokaryotes in agricultural soil." Advances in Agronomy 96 (2007): 249-305.
Author
Page authored by Kate Glanville & Di Liang, students of Microbial Ecology at Michigan State University.