Machine Learning Approach to Antibiotic Discovery
Summary
By Reed Crocker
Biology 238: Microbiology
Spring 2020
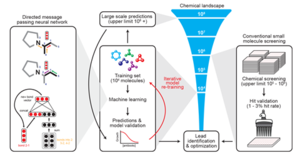
Antibiotics are essential for the modern practice of medicine. However, the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria present new challenges to paradigm in medical treatment. Discovery and development of novel antibiotics is not meeting the pace of microbial resistance. The arms race against pathogenic bacteria has prompted significant research into new modes of antibiotic discovery. One rapidly expanding sector of this research uses a high throughput, machine learning approach to predict candidate antibiotics in silico.
Sample citations: [1]
[2]
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
To repeat the citation for other statements, the reference needs to have a names: "<ref name=aa>"
The repeated citation works like this, with a back slash.[1]
Traditional Discovery Methods
Research about how the gradient control enables higher tolerance.
Advantages of Machine Learning in Antibiotic Discovery
High throughput, less costly, quicker.
Future
Where this research might continue to.
Section 4
Conclusion
References
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski, 2018, Kenyon College.
