Magnetotactic Bacteria: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
[[Image:M. gryphiswaldense.png|thumb|300px|right| Electron micrograph of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense cells containing chains of magnetite crystals (top) and magnified section of crystal chain (bottom). By Caulobacter subvibrioides (Diskussion) GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:M. gryphiswaldense.png|thumb|300px|right| Electron micrograph of <i>Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense</i> cells containing chains of magnetite crystals (top) and magnified section of crystal chain (bottom). By Caulobacter subvibrioides (Diskussion) GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
Revision as of 00:07, 24 March 2015
Introduction
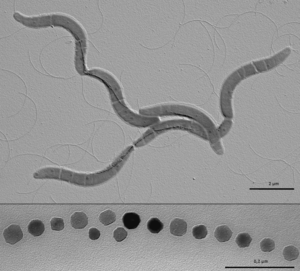
Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense (also referred to as MSR-1) is a gram negative magnetotactic bacteria that is found in shallow fresh water and sediment. They are characterized by a spirillial morphology with flagella at each end of the cell. They are able to orient themselves based on Earth’s magnetic field (magnetotaxis) due to special organelles called magnetosomes.
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Magnetotactic Bacteria
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Magnetosome Formation
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Potential Uses
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Conclusion
Overall paper length should be 3,000 words, with at least 3 figures.
References
Edited by student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 238 Microbiology, 2009, Kenyon College.
