Membrane proteins as mechanisms of immune system evasion in Trypanosoma brucei: Difference between revisions
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
Stamatoiua (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Stamatoiua (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==Mechanism of Infection== | ==Mechanism of Infection== | ||
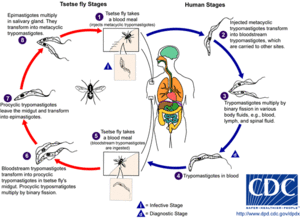
[[Image:AfrTryp_LifeCycle.gif | [[Image:AfrTryp_LifeCycle.gif|300px|center|Life cycle of the parasite from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention.]] | ||
<br>some stuff | <br>some stuff | ||
Revision as of 13:18, 22 April 2013
Introduction
Of all
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Disease Origins
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Include some current research in each topic, with at least one figure showing data.
Mechanism of Infection
some stuff
Protein Cycling
talk about proteins
Drug Interactions
drugs
Future Research
further description of mechanism of action (current data)
Conclusion
Overall paper length should be 3,000 words, with at least 3 figures.
References
Edited by student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 238 Microbiology, 2009, Kenyon College.