Moraxella bovis: Difference between revisions
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
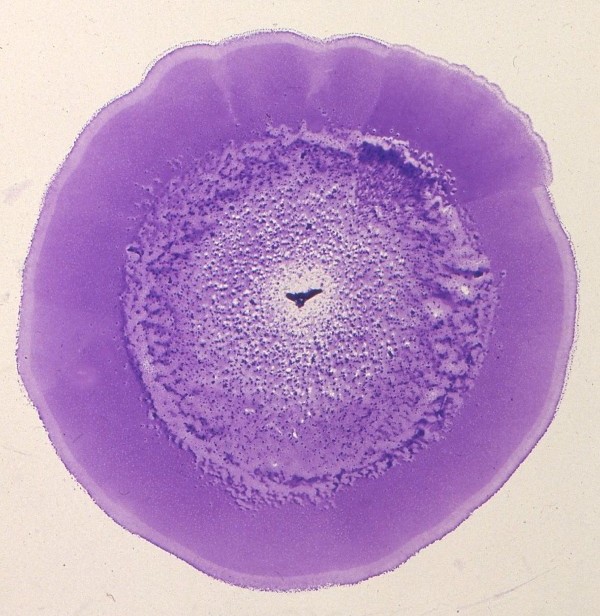
[[Image:McMichael.jpg|frame|left|150px|Photographed and stained with Coomasie Brilliant blue, by John C. McMichael, researcher of ''M. bovis'', who found that by puncturing agar plates when planting culture allows for bacteria to grow in large flat colonies between Petri dish and agar. | [[Image:McMichael.jpg|frame|left|150px|Photographed and stained with Coomasie Brilliant blue, by John C. McMichael, researcher of ''M. bovis'', who found that by puncturing agar plates when planting culture allows for bacteria to grow in large flat colonies between Petri dish and agar. | ||
McMichael, John C. Moraxella Bovis – Evolution in a Petri Dish. Photograph. Http://pandasthumb.org/archives/2009/11/moraxella-bovis.html . 30 Nov. 2009. Web.]] | |||
==Metabolism== | ==Metabolism== | ||
Revision as of 16:53, 26 April 2012
A Microbial Biorealm page on the genus Moraxella bovis
Classification
Higher order taxa
Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Pseudomonadales; Moraxellaceae, Moraxella (2). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=476
Species
Moraxella bovis
Description and significance
Describe the appearance, habitat, etc. of the organism, and why you think it is important.
Genome structure
Describe the size and content of the genome. How many chromosomes? Circular or linear? Other interesting features? What is known about its sequence?
Cell and colony structure
Interesting features of cell structure. Interesting features of colony structure.
Metabolism
Energy source(s); external electron donor(s) (=reductant source(s)); carbon source(s); oxygen classification; important molecules it produces.
Ecology
Habitat; symbiosis; contributions to the environment. metagenomic data link
Pathology
How does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors.
References
1. Angelos, John A., V. Michael Lane, Louise M. Ball, and John F. Hess. "Recombinant Moraxella Bovoculi Cytotoxin-ISCOM Matrix Adjuvanted Vaccine to Prevent Naturally Occurring Infectious Bovine Keratoconjunctivitis." Veterinary Research Communications 34.3 (2010): 229-39. Print. doi: 10.1007/s11259-010-9347-8 . http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2855018/
2. Bergey, D. H., Noel R. Krieg, and John G. Holt. Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins, 1984. Pp 415. http://books.google.com/books?id=0-VqgLiCPFcC&q=moraxella+bovis#v=onepage&q=moraxella&f=false
3. "Genes and Mapped Phenotypes." National Center for Biotechnology Information. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Web. 19 Mar. 2012. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene
4. Highlander, Sarah K., and George M. Weinstock. "HGSC at Baylor College of Medicine." HGSC at Baylor College of Medicine. 27 June 2006. Web. 19 Mar. 2012. http://www.hgsc.bcm.tmc.edu/projects/microbial/microbial-detail.xsp?project_id=123 .
5. McMichael, J. C. "Bacterial Differentiation within Moraxella Bovis Colonies Growing at the Interface of the Agar Medium with the Petri Dish." Microbiology 138.12 (1992): 2687-695. NCBI. Web. 07 Feb. 2012. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-12-2687 . http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1362585
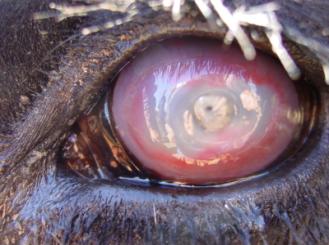
6. R, Craig. New Forest Eye. 2011. Photograph. Http://informedfarmers.com/new-forest-eye-in-beef-cattle/
7. Rodriguez, Jose E., Abebe Hassen, and James Reecy. "Infectious Bovine Keratoconjunctivitis (Pinkeye) Study." Iowa State University, McNay Memorial Research and Demonstration Farm. Web. https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&q=cache:qD2eCA1mRM4J:www.ag.iastate.edu/farms/05reports/mc/InfectiousBovineKeratocon.pdf+&hl=en&gl=us&pid=bl&srcid=ADGEESjMND24hTzgAfzd8lDg_wcztQTqhTTzbkQWBGl_dx2K5np7wwMPk-ybiLvNCkrRL6DxLIwpeugZTLHwSwGkEyYjm4RXyNuAlNjT7LMn4U5MDJ2yYcaCOucV9QNHo_biJ0OOpku_&sig=AHIEtbRslSKkiWDNcee83wG6SrDgc7f0Eg
8. Schaechter, Moselio, John L. Ingraham, and Frederick C. Neidhardt. Microbe. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology, 2006.
Edited by Antonina Planson of Dr. Lisa R. Moore, University of Southern Maine, Department of Biological Sciences, http://www.usm.maine.edu/bio
