Rabies Lyssavirus
Introduction
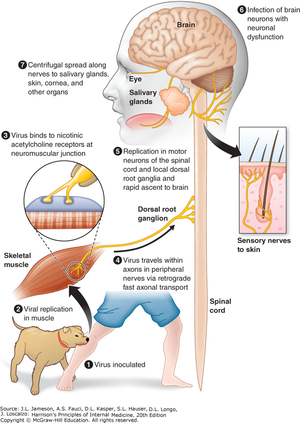
Rabies Lyssavirus, commonly known as the Rabies virus, is a type of neurotropic virus that causes rabies in mammals.[1]
Rabies virus is preventable for humans through vaccination or fast-acting shot that contains rabies immune globulin after one got bitten. Other mammals can also get the vaccination for the prevention of rabies virus.[2]Once the Rabies virus is transmitted through bite or saliva of rabid animals, it will transmit to the central nervous system(CNS)and infects the peripheral nerves. If bites from rabies-infected animals did not receive immediate care, and rabies symptoms start to appear in patients, it is usually fetal.
There is currently no cure for the Rabies virus, and it carries approximately 55,000 lives away each year.[3]
Structure
Rabies Virus (RABV) belongs to the family Rhabdoviruses and the genus Lyssavirus. RABV is a bullet-shaped RNA virus that is about 180 nm in length and 75 nm in width.The "bullet" contains one copy of a enveloped single-stranded non-coding RNA genome.[4]RABV genome encodes five essential structural proteins:
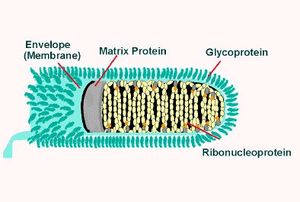
Nucleoprotein(N):
The nucleoprotein encapsidates the non-coding RNA genome to form the viral ribonucleoprotein complex (RNP). The resulting RNP is responsible for the protection of the rabies virus genome from RNA degradation caused by ribonuclease. Other than genome protection, nucleoprotein is also an antigen for viruses due to their group and strain-specific antigenic determinants.[5]
Phosphoprotein(P):
The phosphoprotein (P) plays a key role in the replication of RABV viral RNA by being the cofactor of an essential enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP). The phosphoprotein accomplishes the key RNA synthesis by connecting the nucleoprotein and the polymerase protein in the ribonucleoprotein complex.[6]
Polymerase protein(L):
Polymerase protein is responsible for the transcription of the RABV RNA. During transcription, the L protein will transcribe the viral RNA into leader RNA and five mRNAs that are each capped and polyadenylated. The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase protein is a potential target for rabies treatment because it produces all viral proteins for RABV and requires interaction with other viral proteins for the primary transcription.[7]
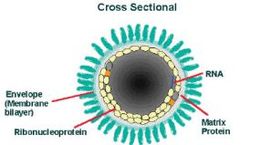
Matrix Protein(M):
It has been known for two decades that matrix protein is responsible for interaction with glycoprotein. M protein also recruit RNPs, whose condensation forms the budding of the bullet-shaped particles.[8] The membrane matrix protein is later known for being a factor for the balance of RABV transcription and replication through inhibiting transcription and stimulating the replication process.[9]
Glycoprotein(G):
Forms glycoprotein spikes on the outer envelope of the virus, which allows the virus to be recognized and aid in its binding to host cells.
The two significant components of the Rabies virus are the ribonucleoprotein complex(RNP) and the surrounding cell envelope.
Out of the five proteins, nucleoprotein(N), Phosphoprotein(P), and Polymerase protein(L) are associated with the RNP. The matrix protein is responsible for covering and keeping the RNP in a condensed form. The rabies virus envelope is constructed of a phospholipid bilayer with glycoprotein spikes.[10]
Evolution

Vaccination

Research, pre and post vaccination, image
Case Studies
Jeanna Giese and California girl 2009, similar Milwaukee treatment. Image

Research
Research directions: permeability of the blood-brain barrier, central nervous system. Rabies virus outer shell, which is unable to cause disease, can be used in other medical field.
Conclusion
Overall text length should be at least 1,000 words (before counting references), with at least 2 images. Include at least 5 references under Reference section.
References
- ↑ Rabies - Symptoms and causes [Internet]. Mayo Clinic. 2019. Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rabies/symptoms-causes/syc-20351821
- ↑ Rabies Vaccine [Internet]. Cdc.gov. 2009. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statements/rabies.pdf
- ↑ Is Rabies Really 100% Fatal? | Viruses101 | Learn Science at Scitable [Internet]. Nature.com. 2013. Available from: https://www.nature.com/scitable/blog/viruses101/is_rabies_really_100_fatal/
- ↑ What is Rabies? | Rabies | CDC [Internet]. Cdc.gov. 2019. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/rabies/about.html.
- ↑ Koser M, McGettigan J, Tan G, Smith M, Koprowski H, Dietzschold B et al. Rabies virus nucleoprotein as a carrier for foreign antigens. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences [Internet]. 2004;101(25):9405-9410. Available from: https://www.pnas.org/content/101/25/9405
- ↑ Okada K, Ito N, Yamaoka S, Masatani T, Ebihara H, Goto H et al. Roles of the Rabies Virus Phosphoprotein Isoforms in Pathogenesis. Journal of Virology [Internet]. 2016;90(18):8226-8237. Available from: https://jvi.asm.org/content/90/18/8226
- ↑ Nakagawa K, Kobayashi Y, Ito N, Suzuki Y, Okada K, Makino M et al. Molecular Function Analysis of Rabies Virus RNA Polymerase L Protein by Using an L Gene-Deficient Virus. Journal of Virology [Internet]. 2017;91(20). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5625484/
- ↑ Mebatsion T, Weiland F, Conzelmann K. Matrix Protein of Rabies Virus Is Responsible for the Assembly and Budding of Bullet-Shaped Particles and Interacts with the Transmembrane Spike Glycoprotein G [Internet]. Journal of Virology. 1999. Available from: https://jvi.asm.org/content/73/1/242.long
- ↑ Finke S, Mueller-Waldeck R, Conzelmann K. Rabies virus matrix protein regulates the balance of virus transcription and replication. Journal of General Virology [Internet]. 2003;84(6):1613-1621. Available from: https://www.microbiologyresearch.org/docserver/fulltext/jgv/84/6/1613.pdf?expires=1575256460&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=8E3AA286D649C7B0CAF0AAF05D0D07DC
- ↑ What is Rabies? | Rabies | CDC [Internet]. Cdc.gov. 2019. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/rabies/about.html.
Edited by Yangyang Liu, student of Joan Slonczewski for BIOL 116 Information in Living Systems, 2019, Kenyon College.
