The Gut-Brain Axis: The Human Gut Microbiome and Anxiety and Depression: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "==Introduction== thumb|300px|right|The human microbiome is a promising area of research for combating antibiotic resistant microorganisms. Photo credit: [http://www.cdc.gov/ CDC.] <b>By Samantha Lee<br> </b>Humans have evolved throughout the many years with microbes. Microbes play an important role in not only human health but also human disease. The human intestinal tract contains a wide variety of microorganisms, all of which have a...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==Section== | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Mrsa_magn_lg.jpg|thumb|300px|right|Magnified 20,000X, this colorized scanning electron micrograph (SEM) depicts a grouping of methicillin resistant <i>Staphylococcus aureus</i> (MRSA) bacteria. See PHIL 617 for a black and white view of this image. Phoro credit: [http://www.cdc.gov/ CDC.]]] | ||
<b>By | <b>By Firtnam Lastname<br> | ||
<br>At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki.<br><br>The insertion code consists of: | <br>At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki.<br><br>The insertion code consists of: | ||
<br><b>Double brackets:</b> [[ | <br><b>Double brackets:</b> [[ | ||
| Line 24: | Line 18: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Sample citations: | Sample citations: <ref name=aa>[http://www.plosbiology.org/article/fetchObject.action?uri=info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pbio.1000005&representation=PDF Hodgkin, J. and Partridge, F.A. "<i>Caenorhabditis elegans</i> meets microsporidia: the nematode killers from Paris." 2008. PLoS Biology 6:2634-2637.]</ref> | ||
<ref name=aa>[ | <ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3847443/ Bartlett et al.: Oncolytic viruses as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Molecular Cancer 2013 12:103.]</ref> | ||
<ref | |||
<br><br>A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes. | <br><br>A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes. | ||
<br>To repeat the citation for other statements, the reference needs to have a names: "<ref name=aa>" | <br>To repeat the citation for other statements, the reference needs to have a names: "<ref name=aa>" | ||
<br> The repeated citation works like this, with a forward slash.<ref name=aa/> | <br> The repeated citation works like this, with a forward slash.<ref name=aa/> | ||
==Section 1== | |||
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<i>Propionibacterium acnes</i> is a gram-positive, fairly slow-growing aerotolerant bacterium. This bacteria is typically linked to the skin condition acne vulgris, commonly known as skin acne. This species is daily commensal and highly present on healthy skin epithelium. Little is detected on the skin of adolescents, specifically those pre-pubescent. This bacterium lives on fatty acids in sebum secreted by hair sebaceous glands in hair follicles. It can also be found in the gastrointestinal biome. | |||
==Section 2== | |||
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.<br> | |||
<br> | |||
==Section 3== | |||
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.<br> | |||
<br> | |||
==Section 4== | |||
==Conclusion== | |||
==References== | |||
<references /> | |||
<br><br>Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by [https://biology.kenyon.edu/slonc/slonc.htm Joan Slonczewski,]at [http://www.kenyon.edu/index.xml Kenyon College,]2024 | |||
Revision as of 18:17, 11 April 2024
Section
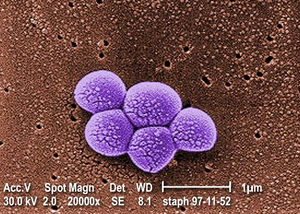
By Firtnam Lastname
At right is a sample image insertion. It works for any image uploaded anywhere to MicrobeWiki.
The insertion code consists of:
Double brackets: [[
Filename: PHIL_1181_lores.jpg
Thumbnail status: |thumb|
Pixel size: |300px|
Placement on page: |right|
Legend/credit: Magnified 20,000X, this colorized scanning electron micrograph (SEM) depicts a grouping of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria. Photo credit: CDC. Every image requires a link to the source.
Closed double brackets: ]]
Other examples:
Bold
Italic
Subscript: H2O
Superscript: Fe3+
Sample citations: [1]
[2]
A citation code consists of a hyperlinked reference within "ref" begin and end codes.
To repeat the citation for other statements, the reference needs to have a names: "<ref name=aa>"
The repeated citation works like this, with a forward slash.[1]
Section 1
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Propionibacterium acnes is a gram-positive, fairly slow-growing aerotolerant bacterium. This bacteria is typically linked to the skin condition acne vulgris, commonly known as skin acne. This species is daily commensal and highly present on healthy skin epithelium. Little is detected on the skin of adolescents, specifically those pre-pubescent. This bacterium lives on fatty acids in sebum secreted by hair sebaceous glands in hair follicles. It can also be found in the gastrointestinal biome.
Section 2
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 3
Include some current research, with at least one figure showing data.
Section 4
Conclusion
References
Authored for BIOL 238 Microbiology, taught by Joan Slonczewski,at Kenyon College,2024
