Search results
From MicrobeWiki, the student-edited microbiology resource
There is a page named "Yersinia pestis" on microbewiki. See also the other search results found.
Page title matches
- [[Image:ypf.jpeg|thumb|'''Y. pestis''' shown at 2000x magnification with fluorescent staining <p> <small>source <p>'''Genus:''' Yersinia </p>11 KB (1,621 words) - 14:04, 13 May 2016
- ...aproteobacteria; Enterobacteriales; Enterobacteriaceae; Yersinia; Yersinia pestis ...d lead to septic shock with high mortality without early treatment (8). Y. pestis CO92 is a very dangerous bacteria and if used in biological warfare it coul10 KB (1,612 words) - 22:36, 29 December 2011
- ...>. From: www.mirror.co.uk [https://www.google.it/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=yersinia+pestis&source=images&cd=&docid=IAy0uj-NhdAv6M&tbnid=S-ORhEmY5ud0GM:&ved=0CAUQjRw&u | Genus = <i>Yersinia</i>32 KB (4,687 words) - 19:14, 11 February 2016
File:Yersinia pestis 1.jpg (523 × 476 (284 KB)) - 15:24, 20 April 2015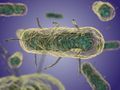
File:3D Yersinia pestis model.jpeg (600 × 449 (64 KB)) - 06:55, 17 July 2014- ...uelaw.jpeg|thumb|1,000 × 233 pixels|right|Figure 1: This is an image of Y. pestis under scanning microscopy [SCIENCE ARTWORK/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://ww <b>Genus:</b> Yersinia18 KB (2,615 words) - 02:01, 18 April 2023
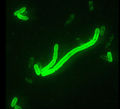
File:Nnate-immunity-subversion-by-Yersinia-pestis-Schematic-representation-of-Y-pestis.png ...>https://www.researchgate.net/figure/nnate-immunity-subversion-by-Yersinia-pestis-Schematic-representation-of-Y-pestis_fig2_332179853</ref>]](850 × 1,038 (233 KB)) - 05:53, 19 April 2022- <br>• <b>Genus:</b> Yersinia ...umb|300px|right|Figure 1. Direct Fluorescent antibody stain of <i>Yersinia pestis</i> at 200x magnification, courtesy of the CDC, US government public domain22 KB (3,592 words) - 15:38, 2 October 2015
- 1 KB (223 words) - 14:32, 1 May 2015
Page text matches

File:Graphical Abstract Rascovan et al .png ..., and Simon Rasmussen. “Emergence and Spread of Basal Lineages of Yersinia Pestis during the Neolithic Decline.” 2019. Cell 176 (1–2): 295-305.e10.(776 × 786 (661 KB)) - 21:01, 14 April 2024
File:Yersinia-plague-food-poisoning-and-a-potential-cancer-treatment.jpg ...ancer-treatment.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Image of a flea with mass of Yersinia pestis cells in its midsection.]] Credit: Author Necrophorus. Published October 20(700 × 476 (43 KB)) - 02:34, 18 April 2022
File:41586 2001 Article BF35097083 Fig1 HTML.jpg ...icle_BF35097083_Fig1_HTML.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Genome sequence of Yersinia pestis strain CO92. ]](600 × 588 (80 KB)) - 02:43, 18 April 2022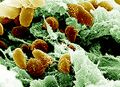
File:Yersinia pestis.jpg Image of Yersinia pestis using electron microscopy. Fake coloring was used to improve visualization.(300 × 217 (65 KB)) - 02:10, 18 April 2022
File:Flealaw.png ...psylla montana (a ground squirrel flea) infected and blocked with Yersinia pestis. [Mitchell et al, CC-BY 4.0, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/](700 × 503 (326 KB)) - 01:17, 17 April 2023
File:41435 2019 65 Fig1 HTML.png ...These events involving gene loss and gain resulted in the divergence of Y. pestis from Y. pseudotuberculosis. <ref>https://www.nature.com/articles/s41435-019(1,750 × 879 (134 KB)) - 05:39, 19 April 2022
File:Nnate-immunity-subversion-by-Yersinia-pestis-Schematic-representation-of-Y-pestis.png ...>https://www.researchgate.net/figure/nnate-immunity-subversion-by-Yersinia-pestis-Schematic-representation-of-Y-pestis_fig2_332179853</ref>]](850 × 1,038 (233 KB)) - 05:53, 19 April 2022- [[Image:yersinia_1.jpg|thumb|350px|right|Image of ''Yersinia pestis.'' From [http://www.kvarkadabra.net/index.html?/biologija/teksti/biolosko_o ''Yersinia pestis CO92, Y. pestis, Y. enterocolitica, Y. pseudotuberculosis''6 KB (947 words) - 20:57, 6 August 2010
- [[Yersinia Pestis and the Plague]], by Ian Law1 KB (135 words) - 18:01, 8 January 2024
- [[Image:ypf.jpeg|thumb|'''Y. pestis''' shown at 2000x magnification with fluorescent staining <p> <small>source <p>'''Genus:''' Yersinia </p>11 KB (1,621 words) - 14:04, 13 May 2016
- ...aproteobacteria; Enterobacteriales; Enterobacteriaceae; Yersinia; Yersinia pestis ...d lead to septic shock with high mortality without early treatment (8). Y. pestis CO92 is a very dangerous bacteria and if used in biological warfare it coul10 KB (1,612 words) - 22:36, 29 December 2011
- ...ism to spread the disease. When an infectious fleabites human, <i>Yersinia pestis</i> enters blood stream and is drained to lymph nodes, where it multiplies. ...after or without showing bubonic plague symptoms. It occurs as <i>Yersinia pestis</i> population grows in bloodstream, which triggers massive immune response13 KB (2,002 words) - 03:36, 20 August 2010
- Yersinia Pestis and Bioterrorism by Jada Swearingen Yersinia Pestis (also known as the Black Death) is a gram-negative coccobacillus that is tr7 KB (1,034 words) - 01:26, 18 April 2022
- Blake Calcei, [[Yersinia pestis, the History of the Plague and Adaptation to Animal Host]]<br>2 KB (216 words) - 00:47, 25 September 2015
- ''Yersinia pseudotuberculosis'' (1) ''Yersinia pseudotuberculosis'' is a rod-shaped bacteria that has flagella. (16, 17)17 KB (2,360 words) - 19:18, 19 August 2010
- ...uelaw.jpeg|thumb|1,000 × 233 pixels|right|Figure 1: This is an image of Y. pestis under scanning microscopy [SCIENCE ARTWORK/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://ww <b>Genus:</b> Yersinia18 KB (2,615 words) - 02:01, 18 April 2023
- <br>• <b>Genus:</b> Yersinia ...umb|300px|right|Figure 1. Direct Fluorescent antibody stain of <i>Yersinia pestis</i> at 200x magnification, courtesy of the CDC, US government public domain22 KB (3,592 words) - 15:38, 2 October 2015
- ...xample of infection by consumption is the infection of fleas by [[Yersinia pestis]], the bacterium responsible for the plague. The gut is infected when the f ...Y. pestis. that uses three key genes in colonization of the flea gut: ymt (Yersinia murine toxin), gmhA and hms (hemin storage) genes. The ymt gene encodes a p12 KB (1,637 words) - 14:10, 26 April 2021
- ...>. From: www.mirror.co.uk [https://www.google.it/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=yersinia+pestis&source=images&cd=&docid=IAy0uj-NhdAv6M&tbnid=S-ORhEmY5ud0GM:&ved=0CAUQjRw&u | Genus = <i>Yersinia</i>32 KB (4,687 words) - 19:14, 11 February 2016
- ...tively. Plasmid pHCM2 is closely related to the pMT1 plasmid of ''Yersinia pestis'', but lacks the capsular antigen operon and murine toxin genes that are ch ...mes of the two strains are more than 98% similar, and, unlike the ''Y''. ''pestis'' strains KIM and CO92, the organization of the two genomes is very similar6 KB (946 words) - 20:43, 6 August 2010
